The Theory
of Measurements - III
Frame of References
24th December 2024
" Observer first sets the field to make measurements and then experience reality. "
―
"It is known that geometry assumes, as things given, both the notion of space and the first principles of constructions in space. She gives definitions of them which are merely nominal, while the true determinations appear in the form of axioms. The relation of these assumptions remains consequently in darkness; we neither perceive whether and how far their connection is necessary, nor a priori, whether it is possible."
- Bernhard Riemann, On the Hypotheses which lie at the Bases of Geometry.
"In a system of reference rotating relatively to an inert system, the laws of disposition of rigid bodies do not correspond to the rules of Euclidean geometry on account of the Lorentz contraction; thus if we admit non-inert systems we must abandon Euclidean geometry."
- Albert Einstein, Geometry and Experience.
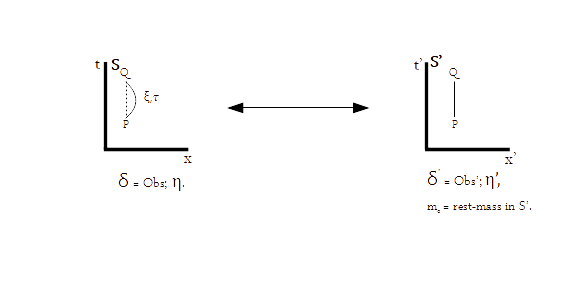
Previously we discussed an example of the State of Measurement, shown below:
We can think of the ocean as the information space, while the Surfboard + Observer is equivalent to a measurement lab with a Hamiltonian H (K.E. + P.E. + Resources), used to measure the information space.
We also keep in mind that even the zero-entropy measurement requires a minimal force and hence the presence of a Lagrangian. In this case the Surfer applies a measurement force to the surfboard, and the resources required are represented by the Lagrangian L (K.E.- P.E.).
Before proceeding any further, let us quickly discuss the Postulates of Special Relativity:
1. Principle of Relativity: Physical Equations must be the same in all inertial frames of reference. Einstein expanded the Principle of Relativity further into the Principle of General Covariance by stating, " The physical equations must be covariant under non-linear coordinate transformations." Which means that the space-time interval ds2 must remain unchanged with the coordinate transformations.
Simply said physics remains the same in all coordinate frames (inertial or non-inertial) in GR, whereas physics remains the same in all inertial coordinate frames in SR.
An important fact to note, is that in SR and GR both, coordinate frames exist i.e. the existence of geometries is implicit, although background independence is a requirement for GR. We assume that the definitions of origin and corresponding basis vectors, are already established either in space or in space-time. (At present we are also not getting into the Diffeomorphism vs Covariance debate either.)
Conventionally, we do not worry about how the geometries are established or what measurements are performed to establish geometries in either inertial or non-inertial coordinate frames.
However that is not the case in a measurement space. We are specifically looking into the establishment of a geometry based on observer's measurements to determine the origin or 0j, and the subsequent motion in the established geometry. Without the precise measurement of the origin, the motion in geometry is not possible.
And since the laws of physics will remain the same for all observers, we can explicitly say that the laws of physics must remain the same in all geometries or all the geometries must follow the laws of nature.
(There we said it, the Motion in Geometry, is the most fundamental problem to solve in the discrete measurement space.)
2. Constancy of Light Speed: The speed of light in vacuum is the same for all observers (coordinate frames), regardless of the motion of light source or observer. This statement puts an upper limit on the speed of light, or any other physical entity in q3 space or our universe. Recall that we incorporated this fact as the maximum efficiency of the observer in S' frame, ηc (η = 1), in j-space:

What the Constancy
of Light Speed implies, is that
the observer with maximum
efficiency ηc, sets the
constraints on the measurement
space, which are to be obeyed by
all other observers with
measurement efficiencies less than
ηc.
*****
The very first thing we are going to do, is to assign frames of reference to observers. The frame S, is assigned to the observer making measurements, ObsM, in this case the surfer. The frame S' is assigned to the event/observer being measured, in this case the ocean wave.

Next we will notice that the surfer is in the state of measurement in reference frame S, its rest frame, while measuring the events in S'. And each measurement is symbolized by a Measurement Circuit (MCkt), which is in the plane perpendicular to N' in S' frame. We also note that the origins O and O' are not identical.

MCkt determining the normal N' in the reference frame S', plays a very important role in SOM. MCkt depends upon the observer's capability in S-frame, which is defined by observer's Hamiltonian and Lagrangian.
For S-frame, a MCkt is determined by Obsc and followed by every other observer in that frame. (i.e. the definition of the basis vectors in the measurement space for ObsM is determined by Obsc.)
If N' in S'-frame aligns with N in S-frame, we have a zero-entropy, equally finite entropy, measurement. Which is equivalent to saying that if a MCkt can be completed, then the problem of measurement is equivalent to a finite well or a shallow-well problem. However if a MCkt cannot be completed, it is an infinite well or the particle in a box problem1.
So by this time we have probably realized that we were trying to determine the normal N' in S' frame by measuring an infinitesimal area dx⨂dy, based on MCkt, with precision.
An incredibly difficult problem, but when we are stuck in a universe where every entity is in a state of measurement, what choice do we have except to complete the measurement?
*****
Let
us consider the following cases, in an
increasing order of complexity:Galilean/Newtonian motion (Linear Coordinates, Inertial Frames): In this case the observers in S and S' both have nearly equivalent capability and their measurements of the origins in their respective frames are identical. N and N' are perfectly aligned.

This situation represents the physical world we are most familiar with, and our day to day lives. As far as we are concerned, most of the measurements are zero-entropy measurements, and as they say the ignorance is bliss.
Relativistic Motion (Linear Coordinates, Inertial/Non-inertial Frames, SR): As if it was not bad enough, imagine trying to maintain balance on a relativistic ocean wave. The observer in S frame can not align its normal N with N' with complete certainty.

The precision will be gone and the observer in S-frame will have to rely on additional resources, i.e. unless the surfboard (a.k.a. our lab), is turned into a spaceship installed with a Quantum Computer, the equilibrium can not be maintained by the surfer in this condition.
Until now, we have assumed that information contents of the reference frames S and S' are determined by the observer Obsc who has the maximum measurement efficiency. And in our measuring tool set of clocks and rods, both (clocks and rods) are independent of each other (Linear Coordinate Frame). However this is not always the case.
We have also assumed that perfect vacuum exists in S and S' frames. We have not included the possibility of the presence of δ-functions loaded with information content in the measurement space.
When we make measurements in a realistic space-time which is non-local, then the ecosystem of δ-functions must be included, which represents the case of measurements made in a non-linear coordinate system. A non-linear coordinate system means, rods and clocks measurements are not independent of each other
Relativistic Motion (Non-Linear Coordinates, GR):
When we speak of non-linear coordinates, we are discussing the constraints which are placed on the maximum efficiency observer in S frame, Obsc. An example, is the light wave bent by gravitational forces, or gravitational lensing. The surfer which is represented by ObsM, automatically follows these constraints placed on Obsc.
The events being measured are taking place in S' frame. And based on the measurements made by the observer in S-frame, we are trying to establish the geometry and the subsequent motion in geometry.
We assume perfect vacuum in S-frame, but S'-frame has additional δ-functions which will result in a curved space-time. The situation is shown below:

We also note that rather than using conventional infinitesimal area dxdy of classical geometry, we are using basis vectors2. For S'-frame we have a circuit formed by the basis vectors u' and v', which for the notation ease we will simply call u and v.
Next we will take the unit vector n from S-frame and make it travel around this circuit. The initial and final positions of the normal vector n, are given as ni and nf.

To define the curvature of the measured space-time, we use the concept of "holonomy". So if there is no δ-function in the measured space i.e. S'-frame, then ni and nf are congruent and the curvature in space-time does not exist i.e. holonomy is zero.
However if a δ-function exists in the S'-frame, a curvature in space-time geometry will exist. In this case ni and nf will not coincide and the holonomy is non-zero.
But what if we can not complete the parallelogram shown above, because the observer in S-frame does not have enough resources to make measurements in S'-frame which has a very complex ecosystem of δ-functions?

Non-zero RCT signifies the existence of the holonomy or the curvature in the measurement space. Here [u,v] defines Commutator Lie bracket for the basis vectors u and v. And the term

It is worthwhile noting that seemingly infinitesimal gap in the measurement circuit in space-time may be equivalent to an infinite spatial distance in Blip, by the time the measurement circuit is completed by either Obsc or ObsM. Pretty spooky isn't it?
And, what if the Action assigned to human DNA runs out, before the eventual Lie bracket could be completely determined by our measurements?
____________________
1. We have discussed similar issue earlier in the context of knots and unknots.
2. Basis vectors are the unit vectors in a coordinate frame. Basis vectors are the entities which gravity-waves tickle, and it results in a tsunami in dx⨂dy plane.
*****
1. We have discussed similar issue earlier in the context of knots and unknots.
2. Basis vectors are the unit vectors in a coordinate frame. Basis vectors are the entities which gravity-waves tickle, and it results in a tsunami in dx⨂dy plane.
..to be
continued

An Ecosystem of δ-Potentials -
IVA
An Ecosystem of δ-Potentials - III
An Ecosystem of δ-Potentials - II
An Ecosystem of δ-Potentials - I
Nutshell-2019
Stitching Measurement Space - III
Stitching Measurement Space - II
Stitching Measurement Space - I
Mass Length & Topology
A Timeless Constant
Space Time and Entropy
Nutshell-2018
Curve of Least Disorder
Möbius & Lorentz Transformation - II
Möbius & Lorentz Transformation - I
Knots, DNA & Enzymes
Quantum Comp - III
Nutshell-2017
Quantum Comp - II
Quantum Comp - I
Insincere Symmetry - II
Insincere Symmetry - I
Existence in 3-D
Infinite Source
Nutshell-2016
Quanta-II
Quanta-I
EPR Paradox-II
EPR Paradox-I
De Broglie Equation
Duality in j-space
A Paradox
The Observers
Nutshell-2015
Chiral Symmetry
Sigma-z and I
Spin Matrices
Rationale behind Irrational Numbers
The Ubiquitous z-Axis
An Ecosystem of δ-Potentials - III
An Ecosystem of δ-Potentials - II
An Ecosystem of δ-Potentials - I
Nutshell-2019
Stitching Measurement Space - III
Stitching Measurement Space - II
Stitching Measurement Space - I
Mass Length & Topology
A Timeless Constant
Space Time and Entropy
Nutshell-2018
Curve of Least Disorder
Möbius & Lorentz Transformation - II
Möbius & Lorentz Transformation - I
Knots, DNA & Enzymes
Quantum Comp - III
Nutshell-2017
Quantum Comp - II
Quantum Comp - I
Insincere Symmetry - II
Insincere Symmetry - I
Existence in 3-D
Infinite Source
Nutshell-2016
Quanta-II
Quanta-I
EPR Paradox-II
EPR Paradox-I
De Broglie Equation
Duality in j-space
A Paradox
The Observers
Nutshell-2015
Chiral Symmetry
Sigma-z and I
Spin Matrices
Rationale behind Irrational Numbers
The Ubiquitous z-Axis

Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use. No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits. This is a human-readable summary of (and not a substitute for) the license.


